Millions of workers across the United States will be headed to the polls on Tuesday, November 8, 2022, for the midterm elections. With control of Congress up for grabs for the final two years of President Joe Biden’s first term, several close Senate races, five states considering ballot measures to legalize recreational marijuana, and 36 states holding elections for governor, this midterm election is one of the most highly-anticipated in decades. Early voting numbers in some states already suggest there could be record turnout.
Despite the proliferation of early and mail-in voting, increased interest in this election could drive more employees to request time off from work to vote. Most states require employers to provide at least unpaid leave from work when polls are not open for a reasonable amount of time outside of employees’ work hours. Here is an overview of voting leave requirements across the United States to help employers prepare for Election Day.
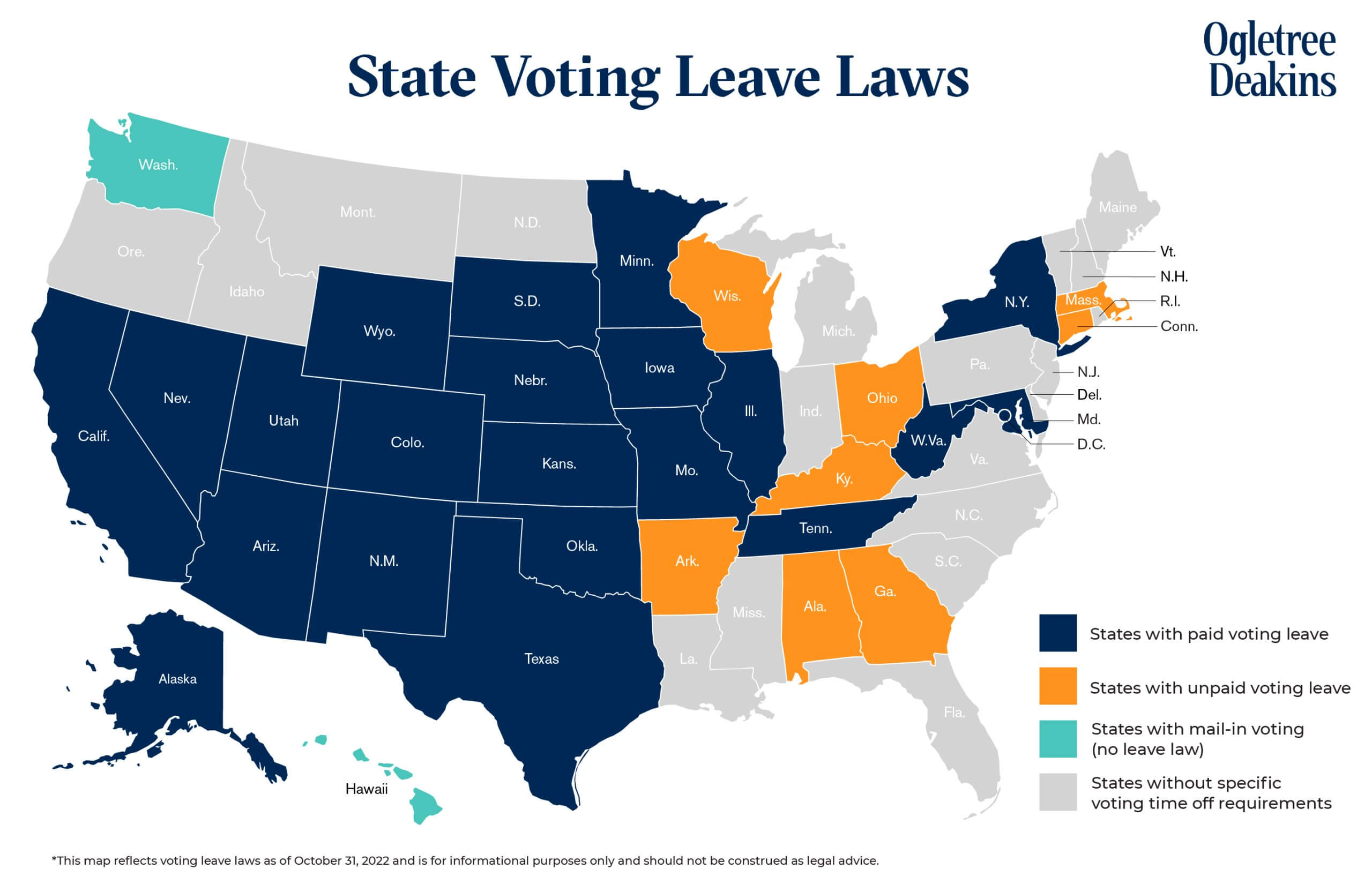
States Without Specific Voting Time Off Requirements
Several states do not require employers to provide any specific leave to allow employees to vote. These include Delaware, Florida, Hawaii, Idaho, Indiana, Louisiana, Maine, Michigan, Montana, New Hampshire, New Jersey, North Carolina, North Dakota, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, South Carolina, Vermont, and Virginia.
While not requiring leave, some of those states more generally protect employees’ rights to vote or participate in politics more generally. For instance, Florida and Mississippi prevent employers from discharging an employee for voting or based on how they voted. Similarly, in Idaho and Michigan, employers may not attempt to influence an employee’s vote by discharging or threatening to discharge an employee from employment.
Delaware and New Jersey prohibit employers from intimidating employees into how to vote or not to vote, and Pennsylvania prohibits employers from interfering with an employee’s right to vote. Louisiana requires that employers with 20 or more employees not make any rule that prohibits an employee from participating in politics. In North Dakota, employers are encouraged, but not required, to allow employees to take leave to vote in all elections when employees’ regular work schedules conflict with the time the polls are open.
Finally, Washington and Hawaii do not have specific voting leave laws, but both conduct elections by mail, eliminating the need to take leave to wait at the polls. Hawaii repealed a prior law providing for up to two hours of voting leave when it switched to vote-by-mail for all statewide elections with the 2020 primary election.
States With Unpaid Voting Leave Laws
Several states require employers to provide employees with some amount of unpaid leave to allow them to vote. Connecticut joined this list of states in June 2021, requiring employers to provide all employees with two hours of unpaid leave to vote in a covered election, though employees must provide the employer notice of the need to take the time off at least two days prior to the election. However, the law is set to sunset on June 30, 2024.
Arkansas and Ohio generally require employees to allow employees to take a reasonable amount of time off, unpaid, to vote on Election Day. In Alabama, employees are allowed to take up to one hour of leave to vote in primary and general elections if the polls are not open at least two hours before or one hour after an employee’s work shift.
In Georgia, employers must give employees “necessary” time off to vote when employees provide reasonable notice of the need for the leave, however, employers are not required to provide time off for employees who have at least two hours before or after their work shift when polls are open to vote. In Massachusetts, unpaid voting leave applies only to employees working in manufacturing, mechanical, or mercantile establishments, and employers are not required to pay for this leave. Further, employees may only request leave for the first two hours after the polls are open.
Some states provide more than two hours of leave for employees to vote, though employers are not required to pay for it. In Wisconsin, employers must allow employees to take up to three consecutive hours of unpaid leave to vote. Employers may not deny a request for this leave, but may designate the specific time of the absence. Kentucky provides the most time for voting leave, requiring employers to allow employees to take unpaid leave for a reasonable time, but not less than four hours, to vote or apply for an absentee ballot. Still, employees must request leave in advance and specify the hours to be used.
States With Paid Voting Leave Laws
Employers in a number of states are required to provide paid time off for employees to vote, at least in circumstances where polls are not open outside of an employee’s regular work hours. Alaska requires employers to allow employees who do not have two consecutive nonworking hours while the polls are open to take off as much work time as necessary to vote “without loss of pay.” Similarly, in Texas, employers must allow employees to take paid time off to vote, unless the polls are not open for two consecutive hours outside of an employee’s working hours.
In Minnesota, employees must have “the time necessary” to go to their designated polling place and return to work on Election Day. In Nevada, employees may request “sufficient” leave time to vote on Election Day, which is determined by the distance of the polling place from the employee’s workplace (1 hour for up to 2 miles; 2 hours for greater than 2 and up to 10 miles; and 3 hours for more than 10 miles). Wyoming requires employers to provide for one hour of leave other than a meal break to vote in a general, primary, or special congressional election unless polls are open for at least three consecutive hours outside of an employee’s work shift.
Many states provide for up to two paid hours of leave for voting. These include: California, Colorado, District of Columbia, Illinois, Iowa, Kansas, Maryland, Nebraska, New Mexico, New York, Oklahoma, South Dakota, and Utah. Iowa, in 2021, reduced the paid leave from three hours to two. On the other hand, D.C. joined the states providing for up to two hours of paid leave for voting in October 2020. The D.C. law further requires employers to post a “Time Off to Vote” notice in a conspicuous location in the workplace. In New York, employers must give employees two hours of paid leave if employees do not have at least four consecutive nonworking hours to vote while polls are open. New Mexico’s leave law includes elections for Native American nations, tribes, or pueblos.
A handful of states provide for up to three hours of paid leave to vote if necessary, including Arizona, Missouri, Tennessee, and West Virginia. These states require employees provide notice of the need for leave prior to Election Day.
Employers may want to prepare for employees to take the leave time afforded by these laws to vote in the November elections.
Further information on state leave laws is available in the firm’s OD Comply: State Leave Laws subscription materials, which are updated and provided to OD Comply subscribers as the law changes.